|
|
Software Matrox MIL 10
REMARK: OBSOLETE PRODUCT.
DescriptionMatrox Imaging Library (MIL) is a comprehensive collection of software tools for developing machine vision, image analysis, and medical imaging applications. MIL includes tools for every step in the process, from application feasibility to prototyping, through to development and ultimately deployment. The toolkit features interactive software and programming functions for image capture, processing, analysis, annotation, display, and archiving. These tools are designed to enhance productivity, thereby reducing the time and effort required to bring your solution to market. Image capture, processing, and analysis operations have the accuracy and robustness needed to tackle the most demanding applications. These operations are also carefully optimized for speed to address the severe time constraints encountered in many applications. MIL at a glance:
About MIL development First released in 1993, MIL has evolved to keep pace with and foresee emerging industry requirements. It was conceived with an easy-to-use, coherent API that has stood the test of time. MIL pioneered the concept of hardware independence with the same API for different image acquisition and processing platforms. A team of highly-skilled and dedicated computer scientists, mathematicians, software engineers, and physicists continue to maintain and enhance MIL. MIL is maintained and developed using industry recognized best practices, including peer review, user involvement, and daily builds. Users are asked to evaluate and report on new tools and enhancements, which strengthens and validates releases. Ongoing MIL development is integrated and tested as a whole on a daily basis. About MIL SQA In addition to the thorough manual testing performed prior to each release, MIL continuously undergoes automated testing during the course of its development. The automated validation suite—consisting of both systematic and random tests—verifies the accuracy, precision, robustness, and speed of image processing and analysis operations. Results, where applicable, are compared against those of previous releases to ensure that performance remains consistent. The automated validation suite runs continuously on hundreds of systems simultaneously, rapidly providing wide-ranging test coverage. The systematic tests are performed on a large database of images representing a broad sample of real-world applications. MIL 10 highlights:
Technical specificationTOOLS Field-proven tools Central to MIL are tools for calibrating, enhancing and transforming images, locating objects, extracting and measuring features, reading character strings, and decoding and verifying identification marks. These tools are carefully developed to provide outstanding performance and reliability, and can be used within a single computer system or distributed across several computer systems. Pattern recognition MIL includes two tools for performing pattern recognition: Pattern Matching and Geometric Model Finder (GMF). These tools are primarily used to locate complex objects for guiding a gantry, stage, or robot, or for directing subsequent measurement operations. The Pattern Matching tool is based on normalized grayscale correlation (NGC), a classical technique that finds a pattern by looking for a similar spatial distribution of intensity. A hierarchical search strategy lets this tool very quickly and reliably locate a pattern, including multiple occurrences, which are translated and slightly rotated, with sub-pixel accuracy. The tool performs well when scene lighting changes uniformly, which is useful for dealing with attenuating illumination. A pattern can be trained manually or determined automatically for alignment. Search parameters can be manually adjusted and patterns can be manually edited to tailor performance.
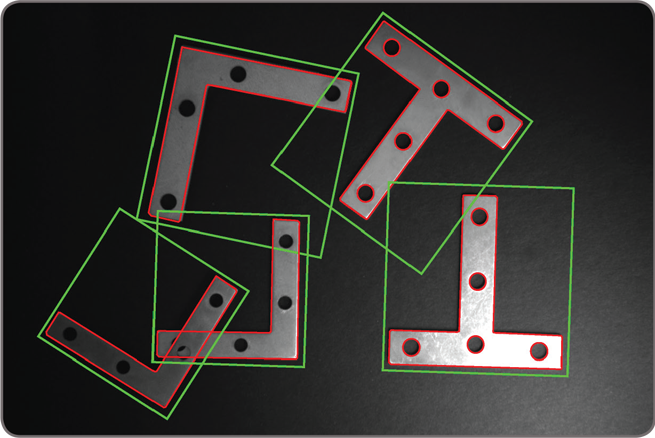
The GMF tool uses geometric features (e.g., contours) to find an object. The tool quickly and reliably finds multiple models—including multiple occurrences—that are translated, rotated, and/or scaled with sub-pixel accuracy. GMF locates an object that is partially missing and continues to perform when a scene is subject to uneven changes in illumination, thus relaxing lighting requirements. A model can be trained manually from an image, obtained from a CAD file, or determined automatically for alignment. A model can also be obtained from the Edge Finder tool, where the geometric features are defined by color boundaries and crests or ridges in addition to contours. Physical setup requirements are eased when GMF is used in conjunction with the Calibration tool as models become independent of camera position. GMF parameters can be manually adjusted and models can be manually edited to tailor performance.
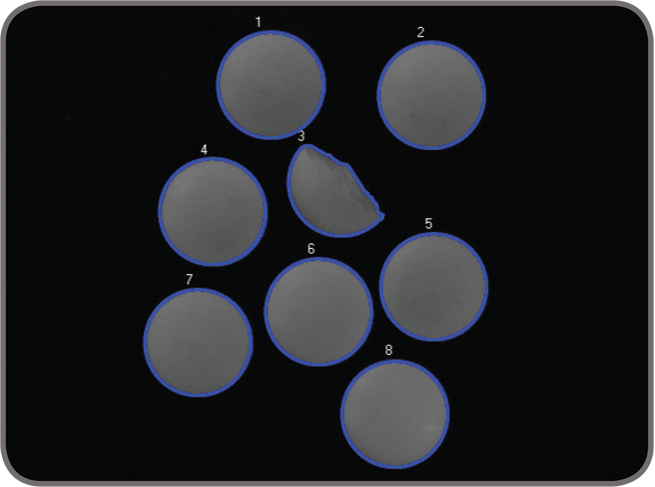
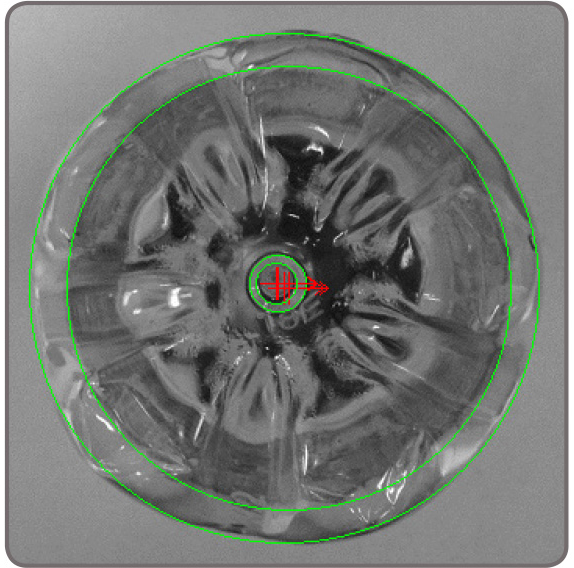
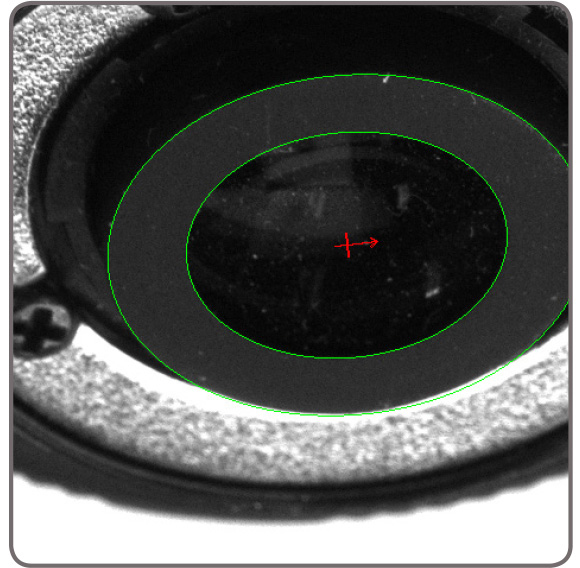
Shape finding The GMF tool includes dedicated modes for finding circles, ellipses, rectangles, and line segments. These modes use the same advanced edge-based technique to locate one or more occurrences of any size—including ones within another for circles, ellipses and rectangles. Circle finding is defined by the anticipated radius, the possible scale range, and the number of expected occurrences.
Ellipse and rectangle finding are defined by the anticipated width and height, the possible scale and aspect ratio ranges, and the number of expected occurrences.
Line segment finding is defined by the anticipated length and the number of expected occurrences.
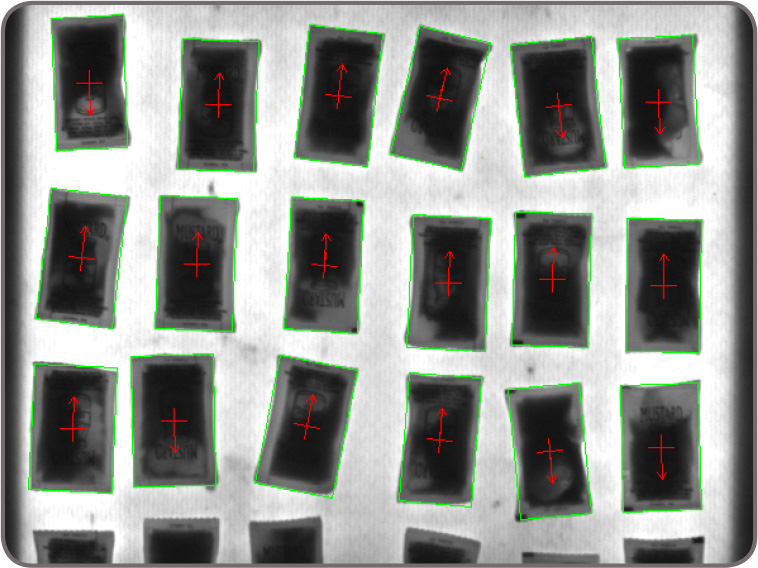
Continuous and broken edges lying within an adjustable variation tolerance produce the requested shape. The shape finding tool returns the total number of found occurrences; for each occurrence, the tool provides the center position and score relative to the reference. It also gives the radius and scale for circles, the angle, aspect ratio, width, and scale for ellipses and rectangles, and the start and end positions as well as the length for line segments. These specialized modes are generally faster and more robust at finding the specific shapes than generic pattern recognition. Feature extraction and analysis MIL provides a choice of tools for image analysis: Blob Analysis and Edge Finder. These tools are used to identify and measure basic features for determining object presence and location, and to further examine objects. The Blob Analysis tool works on segmented binary images, where objects are previously separated from the background and one another. The tool—using run-length encoding—quickly identifies blobs and can measure over 50 binary and grayscale characteristics. Measurements can be used to sort and select blobs. The tool also reconstructs and merges blobs, which is useful when working with blobs that straddle successive images.
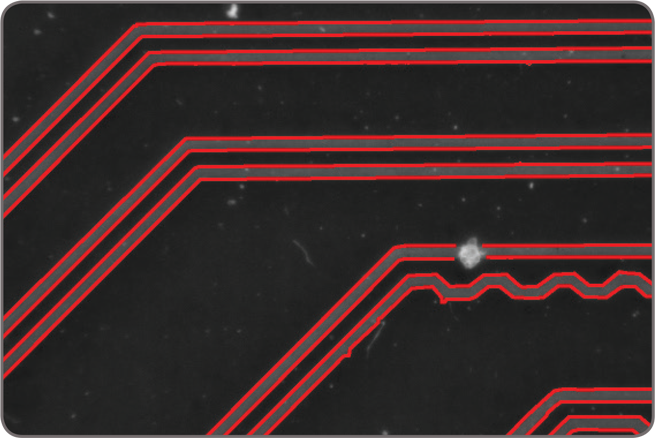
The Edge Finder tool is well suited for scenes with changing, uneven illumination. The tool—using a gradient-based (as well as a Hessian-based) approach—quickly identifies contours, as well as crests or ridges, in monochrome or color images and can measure over 50 characteristics with sub-pixel accuracy. Measurements can be used to sort and select edges. The edge extraction method can be adjusted to tailor performance.
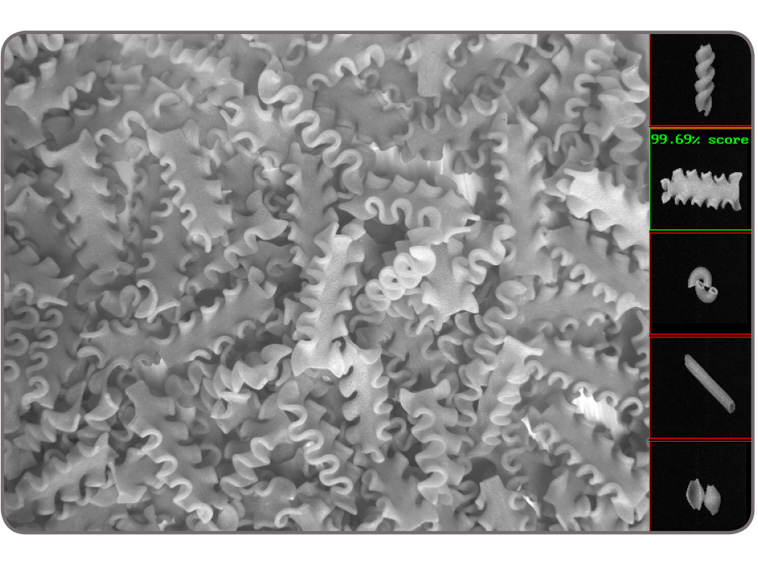
Classification MIL includes a Classification tool for automatically categorizing image content using machine learning. It makes use of deep learning—specifically convolutional neural network (CNN)—technology for assigning images or image regions to pre-established classes. The tool is particularly well-suited for analyzing images of highly textured, naturally varying, and acceptably deformed goods. The intricate design and training of a neural network is carried out by Matrox Imaging, taking advantage of the accumulated experience, knowledge, and skill of its experts in both machine learning and machine vision. Users simply need to submit an adequate set of images that are representative of the given application, categorized for the desired classes, and roughly distributed evenly among the latter. The prediction or inference with the neural network is then performed exclusively by Matrox Imaging-written code on a mainstream CPU, eliminating the dependence on third-party neural network libraries and the need for specialized GPU hardware.
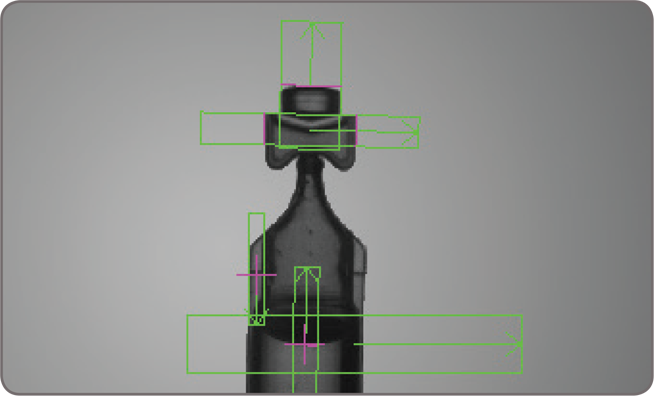
1D and 2D measurements MIL offers three tools for measuring: Measurement, Bead inspection, and Metrology. These tools are predominantly used to assess manufacturing quality. The Measurement tool uses the projection of image intensity to very quickly locate and measure straight edges or stripes, or circles within a carefully defined rectangular region. The tool can make several 1D measurements on edges, stripes, and circles, as well as between edges, stripes, and circles.
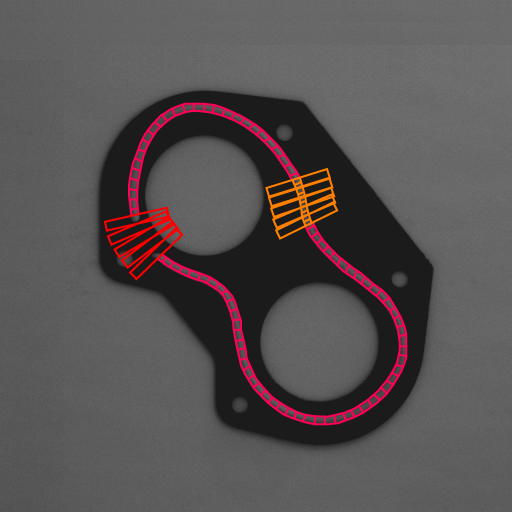
The Bead inspection tool is for inspecting material that is applied as a continuous sinuous bead, such as adhesives and sealants, or the channel where the bead will be applied. The tool identifies discrepancies in length, placement, and width, as well as discontinuities. The Bead inspection tool works by accepting a user-defined coarse path (as a list of points) on a reference bead and then automatically and optimally placing search boxes to form a template. The size and spacing of these search boxes can be modified to change the sampling resolution. The allowable bead width, offset, gap, and overall acceptance measure can be adjusted to meet specific inspection criteria.
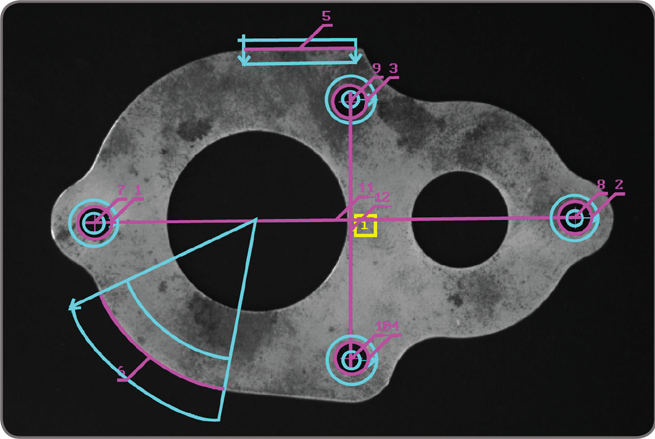
The Metrology tool is intended for 2D geometric dimensioning and tolerancing applications. The tool quickly extracts edges within defined regions to best fit geometric features. It also supports the construction of geometric features derived from measured ones or defined mathematically. Geometric features include arcs, circles, points, and segments. The tool validates tolerances based on the dimensions, positions, and shapes of geometric features. The tool’s effectiveness is maintained when subject to uneven changes in scene illumination, which relaxes lighting requirements. The expected measured and constructed geometric features, along with the tolerances, are kept together in a template, which is easily repositioned using the results of other locating tools. The Metrology tool— along with the use of the Calibration tool—enables templates to be independent of camera position; it can also work on a 3D profile or cross-section image.
Color analysis MIL includes tools to help identify parts, products, and items using color; it can assess quality from color as well as isolate features using color. The Color Distance tool reveals the extent of color differences within and between images. The Color Projection tool separates features from an image based on their colors and can also be used to enhance color to grayscale conversion for subsequent analysis using other grayscale tools. The Color Matching tool determines the best matching color from a collection of samples for each region of interest within an image. A color sample can be specified either interactively from an image—with the ability to mask out undesired colors—or using numerical values.
A color sample can be a single color or a distribution of colors (i.e., histogram). The color matching method and the interpretation of color differences can be manually adjusted to suit particular application requirements. The Color Matching tool can also match each image pixel to color samples to segment the image into appropriate elements for further analysis using other tools.
MIL includes color-relative calibration to correct color appearance due to differences in lighting and image sensing, thus enabling consistent performance over time and across systems. Three methods are provided: Histogram-based, sample-to-sample, and global mean variance. The first method is unsupervised, only requiring that the reference and training images have similar contents. The second method is semi-supervised, requiring the correspondence between color samples on reference and training images, typically of a color chart. The third method is best suited for dealing with color drift and relies on global color distribution.
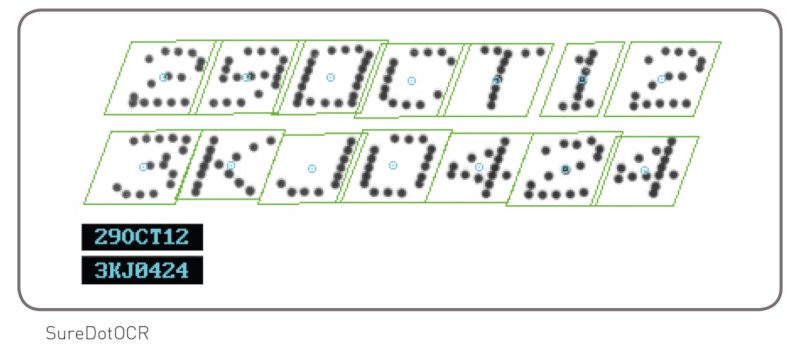
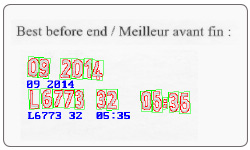
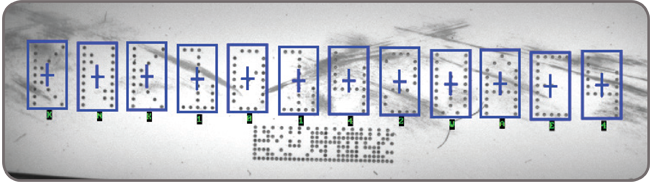
Character recognition MIL provides three tools for character recognition: SureDotOCR, String Reader, and OCR. These tools combine to read text that is engraved, etched, marked, printed, punched or stamped on surfaces. The SureDotOCR tool is uniquely designed for the specific challenge of reading dot-matrix text produced by inkjet printers. Its use is straightforward—users simply need to specify the dot size, the number of expected characters in a text string, and the dimension, but not the location, of the text region. The tool reads text at any angle, with varying contrast, and/or on an uneven background. It interprets distorted and touching characters as well as characters of varying scale. The tool recognizes punctuation marks and blank spaces. It supports the creation and editing of character fonts while including predefined fonts. The tool automatically handles multiple lines of text where each line can utilize a different font. The ability to set user-defined constraints, overall and at specific character positions, further enhances recognition rates. The SureDotOCR tool provides greater robustness and flexibility than case-specific techniques that convert dot-matrix characters into solid ones for reading with traditional character recognition tools.
The String Reader tool is based on a sophisticated technique that uses geometric features to quickly locate and read text made up of solid characters in images where these characters are well separated from the background and from one another. The tool handles text strings with a known or unknown number of evenly or proportionally spaced characters. It accommodates changes in character angle with respect to the string, aspect ratio, scale, and skew, as well as contrast reversal. Strings can be located across multiple lines and at a slight angle. The tool reads from multiple pre-defined (TrueType™ and Postscript™) or user-defined Latin-based fonts. Also included are ready-made Latin-based unified contexts for automatic number plate recognition (ANPR) and machine print. In addition, strings can be subject to user-defined constraints, overall and at specific character positions, to further increase recognition rates. The tool is designed for ease-of-use and includes String Expert, a utility to help fine-tune settings and troubleshoot poor results.
The OCR tool utilizes a template matching method to very quickly read text with a known number of evenly spaced characters. Once calibrated, the tool reliably reads text strings with a consistent character size even if the strings themselves are at an angle. Characters can come from one of the provided OCR-A, OCR-B, MICR CMC-7, MICR E-13B, SEMI M12-92, and SEMI M13-88 fonts or a user-defined font. Strings can be subject to user-defined constraints, overall and at specific character positions, to further increase recognition rates.
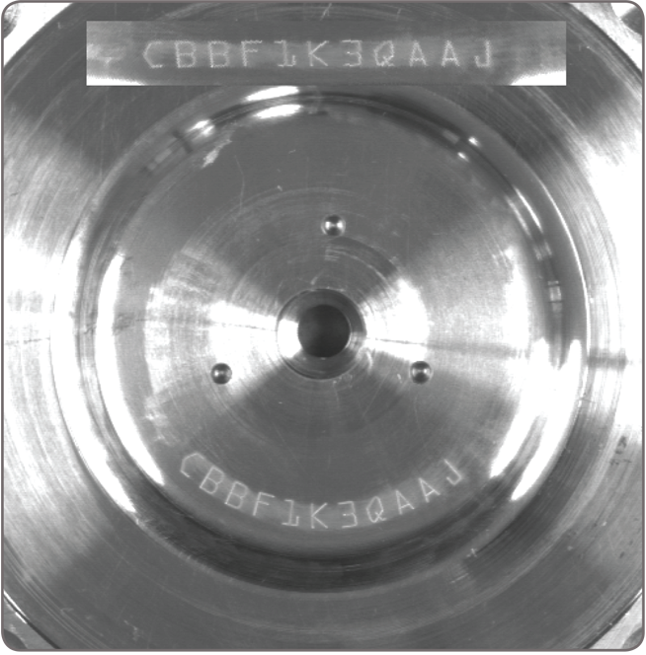
1D and 2D code reading and verification MIL offers Code Reader, a fast and dependable tool for locating and reading 1D, 2D, and composite identification marks. The tool handles rotated, scaled, and degraded codes in tough lighting conditions. It simultaneously reads multiple 1D and DataMatrix codes as well as small codes found in complex scenes. It can automatically determine a 1D code type and the optimal settings from a training set. The tool can return the orientation, position, and size of a code. In addition to reading, the tool can also be used to verify the quality of a code based on the ANSI/AIM and ISO/IEC grading standards.
Registration MIL has a tool set for handling the registration or fusion of images for various objectives. A stitching tool is available for transforming images taken from different vantage points into a unified scene, which would be impractical or impossible to achieve using a single camera. It can also align an image to a reference for subsequent inspection. The tool contends with not only translation, but also with perspective, including scale. Alignment to a reference image or to neighboring images is performed with sub-pixel accuracy and is robust to local changes in contrast and intensity. In addition, the tool can be used for super-resolution where a sharper image is created from a series of images taken from roughly the same vantage point, which is useful for dealing with movement such as mechanical vibration.
Separate extended depth of field and depth-from-focus tools are on hand to produce, respectively, a single all-in-focus image and an index image from a series of images of a motionless scene taken at different focus points. The index image can subsequently be used to infer depth.
A photometric stereo tool is also available to produce an image that emphasizes surface irregularities—such as embossed or engraved features, scratches, or indentations—from a series of images taken with directional illumination as driven by a Light Sequence Switch (LSS) from CCS, a LED Light Manager (LLM) from Smart Vision Lights, or similar light controller.
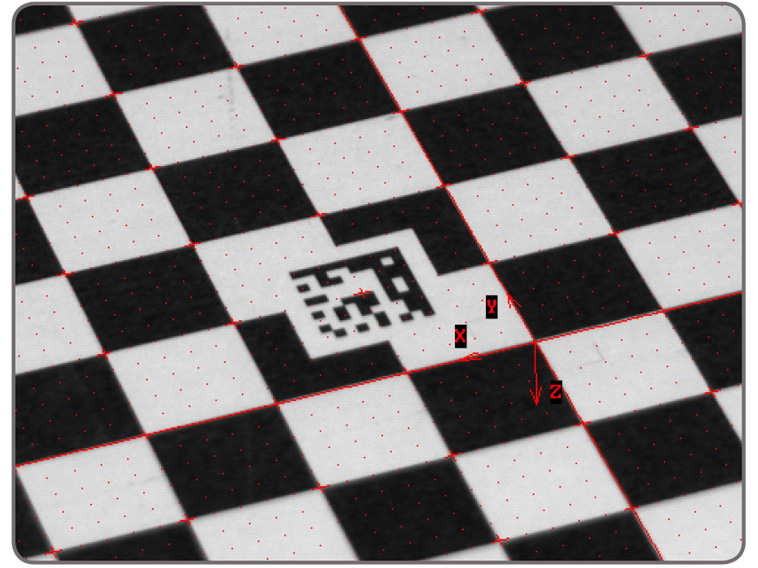
2D calibration Calibration is a routine requirement for imaging. MIL includes a 2D calibration tool to convert results (i.e., positions and measurements) from pixel to real-world units and vice-versa. The tool can compensate results, and even an image itself, for camera lens and perspective distortions. Calibration is achieved using an image of a grid or chessboard target, or just a list of known points. Calibration can be achieved from a partially-visible target. MIL also supports encoded targets that relay target characteristics—including coordinate system origin and axes—to further automate the calibration process.
Image processing primitives A professional imaging toolkit must include a complete set of operators for enhancing and transforming images, and for retrieving statistics in preparation for ensuing analysis. MIL includes an extensive list of fast operators for arithmetic, Bayer interpolation, color space conversion, de-interlacing, spatial and temporal filtering, geometric transformations, histogram, logic, lookup table (LUT) mapping, morphology, orientation, projection, segmentation, statistics, thresholding, and wavelets.
Image compression and video encoding MIL provides image compression and video encoding for optimizing storage and transmission requirements. Lossy and lossless JPEG and JPEG2000 image compression and H.264 video encoding are supported. H.264 support can leverage Intel Quick Sync Video technology for encoding multiple high-definition video streams in real-time. MIL saves and loads compressed images individually using the JPG and JP2 file formats or as a sequence using the AVI file format. The H.264 elementary stream can be stored in and recovered from a MP4 format file. Compression and encoding settings can be adjusted for different size versus quality. Fully optimized for speed MIL image processing and analysis operations are optimized by Matrox Imaging to take full advantage of Intel SIMD instructions —including AVX2— as well as multi-core CPU and multi-CPU system architectures, to perform at top speed. MIL automatically dispatches operations across the number of processor cores needed to achieve maximum performance. Alternatively, it gives programmers control over the number of processor cores assigned to perform a given operation. In addition, MIL is able to offload from the host CPU and even accelerate certain image processing operations when used with Matrox Imaging processing hardware with FPGA technology.
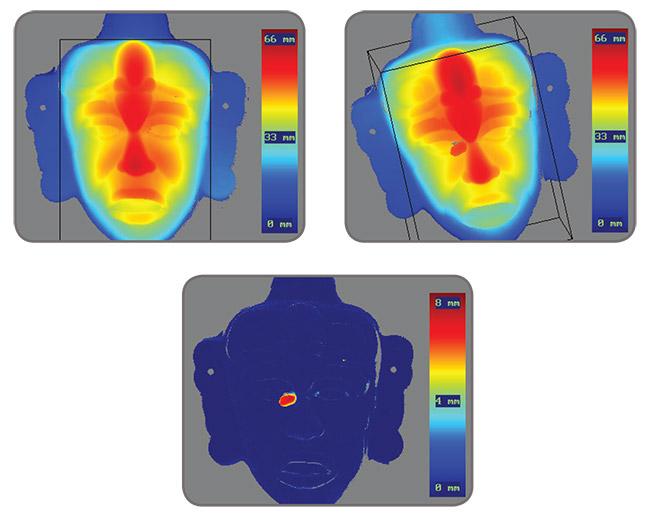
3D imaging tools: 3D profiling Profiling is a widely used 3D scanning technique for industrial inspection and measurement. Based on the principle of triangulation, profiling consists of looking at the alteration to a beam as it is projected onto an object. It relies on movement to accumulate profiles and produce a 3D point cloud. The point cloud can then be projected onto a plane to produce a depth map, a 2D image that replaces intensity values with depth data.
MIL can compute the 3D profiles from a scanning setup based on a discrete sheet-of-light source (e.g., laser) and a conventional 2D camera. A calculator is included to establish the camera, lens, and alignment needed to achieve the desired measurement resolution and range. MIL provides controls to tailor the beam extraction process. Also included in MIL are straightforward calibration methods and associated tools to produce a partially corrected depth map for accurate analysis of depth only or a fully-corrected depth map for accurate analysis along all three axes. Both cases provide measurements in real-world units. The calibration service provided in MIL is able to combine multiple sheet-of-light sources and 2D camera pairs3 to work as one, thus avoiding the need for post alignment and merger. Such configurations are useful to limit occlusion, increase scan density, and image the whole volume of an object. MIL can also output the initial point cloud for subsequent processing, like surface rendering, using third-party software. MIL can also work with the point cloud or depth map produced by 3D profile sensors from LMI Technologies (Gocator series), Micro-Epsilon, Photonfocus, SmartRay, and SICK (Ranger series). It can also accept the point cloud and depth map produced by stereo cameras like the Chromasens 3DPIXA, 3D snapshot sensors from LMI Technologies (Gocator series) and Photoneo (PhoXi series), and time of flight (ToF) cameras such as the one from Basler. MIL delivers the necessary tools for manipulating and analyzing a depth map: Fitting a plane, filling in gaps, measuring volume, computing deviations, performing arithmetic operations, determining the tilt of an object from one of its planar surfaces, and extracting a cross section. The depth map can also be analyzed using MIL tools like Blob Analysis after applying a height threshold, Pattern Recognition without being affected by illumination variations or surface texture, and Character Recognition when the alphanumeric code to read protrudes from, but has the same color as, the background. A cross section can be analyzed using metrology. MIL includes a tool for the fine alignment of a model and target point cloud. The tool gives a 3D pose of the model in the target point cloud and thus provides the means to perform pose rectification for high-accuracy comparative analysis. If a pose varies too greatly between a model and its target point cloud, prior separate coarse alignment is required by, for example, finding a fiducial mark in 2D. The model point cloud can be obtained from a 3D profile scan generated using MIL, a point cloud, or CAD (PLY or STL) file.
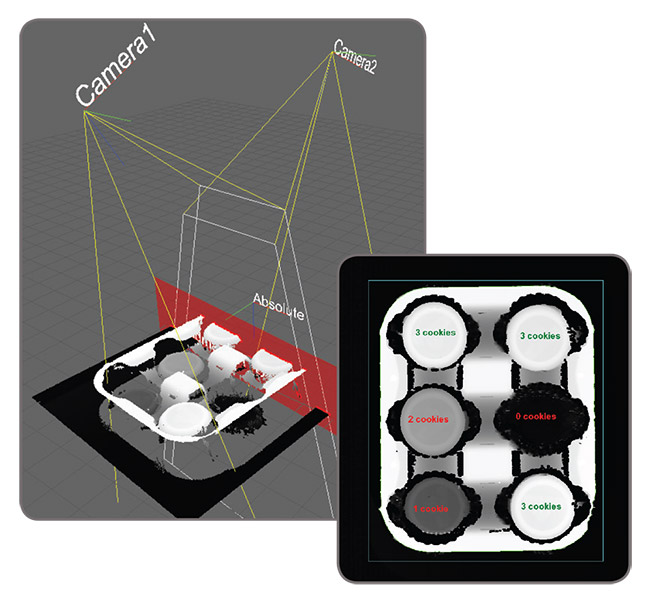
3D vision-guided robotics The need for flexible assembly and material handling is driving the use of robots with machine vision. The full capability of pairing a robot with a vision system is achieved when the two are made to operate together in the 3D workspace. MIL provides the necessary calibration services to position and orient a camera and robot (base) with respect to the absolute coordinate system. It then enables an application to locate a point of interest and even establish an objects’ 3D pose with respect to the absolute coordinate system using multiple views. This is achieved by using other MIL tools for pattern recognition—to find the one identical feature across views, or a minimum of three identical features in case of pose estimation—and then relying on MIL to triangulate the 3D position(s). The pose is established by the application using the geometric relationship of these features, which can come from an object model. Pose estimation can also be performed using a single view by locating a minimum of four object features whose geometric relationship is known beforehand by way of an object model.
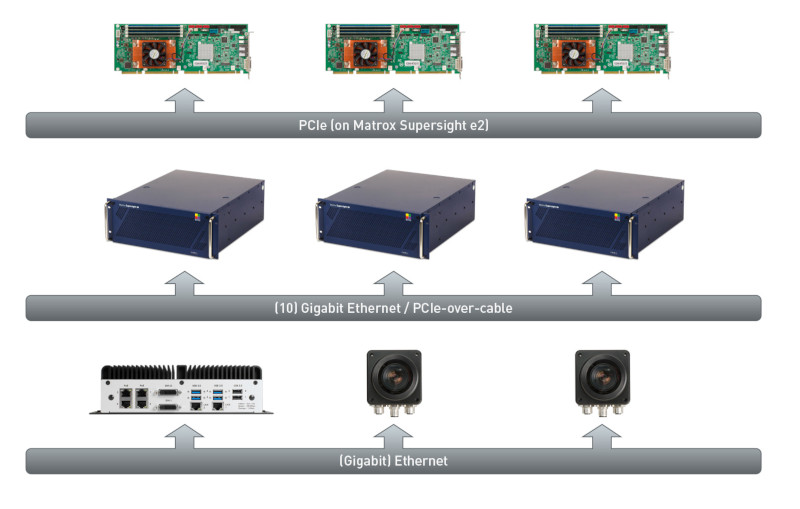
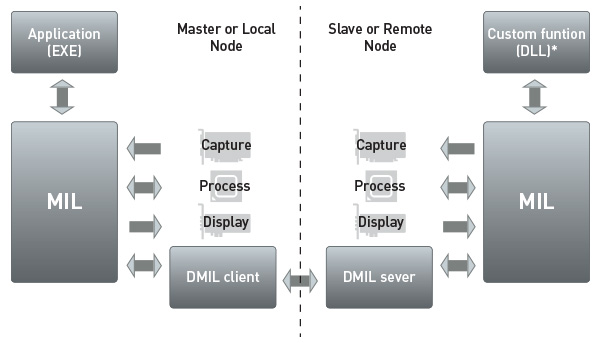
Distributed MIL MIL has the ability to remotely access and control image capture, processing, analysis, display, and archiving. Distributed MIL functionality provides the means to scale an application beyond a single computer and make the most of modern-day HPC clusters for industrial imaging applications. The technology can also be used to control and monitor several PCs and smart cameras deployed on a factory floor. Distributed MIL simplifies distributed application development by providing a seamless method to dispatch MIL (and custom) commands, transfer data, send and receive event notifications (including errors), mirror threads, and perform function callback across systems. It offers low overheads and efficient bandwidth usage, even allowing slave nodes to interact with one another without involving the master node. Distributed MIL also gives developers the means to implement load balancing and failure recovery. It also includes a monitoring mode for supporting the connection to an already running MIL application.
32-bit application on 64-bit Windows
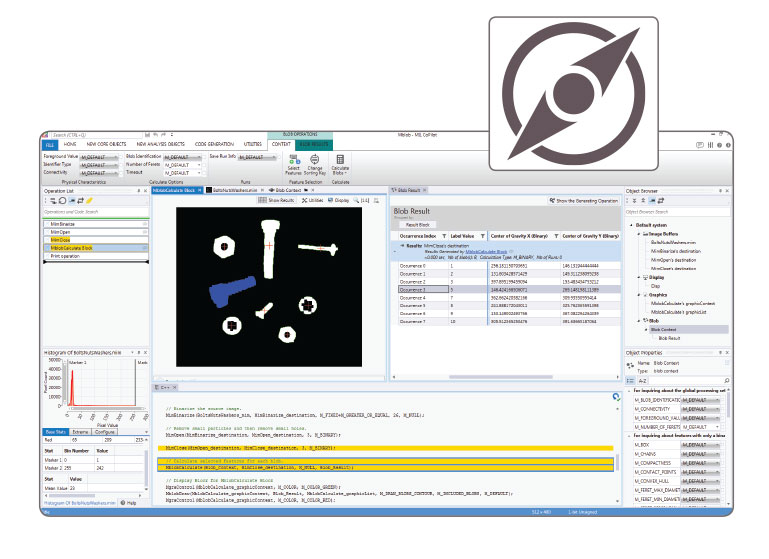
MIL supports the installation and running of a 32-bit application on 64-bit Windows, which is required for third-party legacy software components not natively available in 64-bit. Distributed MIL further enables the 32-bit application to capture video using 64-bit MIL. The 32-bit and 64-bit versions of MIL interact with each other through shared memory. This gives the 32-bit application access to the additional buffering available in the 64-bit address space. PROTOTYPE MIL CoPilot interactive environment Accessible to MIL users is an interactive environment to facilitate and accelerate the evaluation and prototyping of an application. The same environment can also initiate—and therefore shorten—the application development process through the generation of MIL program code. Running on 64-bit Windows, MIL CoPilot provides interactive access to MIL processing and analysis operations via a familiar contextual ribbon menu design. It includes various utilities to study images and help determine the best analysis tools and settings for a given project. Applied operations are recorded in an Operation List, which can be edited at any time. An Object Browser keeps track of MIL objects created during a session and gives convenient access to these at any moment. Non-image results are presented in tabular form and a table entry can be identified directly on the image. The annotation of results onto an image is also configurable. Once an operation sequence is established, it can be converted into functional program code in any language supported by MIL. Program code can be packaged as a Visual Studio project, which in turn can be built and executed without leaving MIL CoPilot. All work carried out in a session is saved as a workspace for future reference and sharing with colleagues.
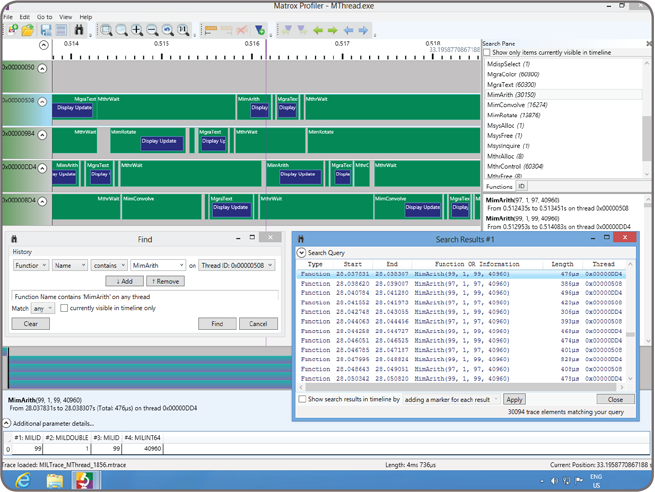
Matrox Profiler Matrox Profiler is a Windows-based utility to post-analyze the execution of a multi-threaded application for performance bottlenecks and synchronization issues. It presents the function calls made over time per application thread on a navigable timeline. Matrox Profiler allows the searching for, and selecting of, specific function calls to see their parameters and execution times. It computes statistics on execution times and presents these on a per function basis. Matrox Profiler tracks not only MIL functions but also suitably tagged user functions. Function tracing can be disabled altogether to safeguard the inner working of a deployed application.
DEVELOP Complete application development environment In addition to image processing, analysis, and archiving tools, MIL includes image capture, annotation, and display functions, which form a cohesive API. The API and accompanying utilities are recognized by the large installed base of users as helpful to facilitate and accelerate application development. Portable API The MIL C API is not only intuitive and straightforward to use but it is also portable. It allows applications to be easily moved from one supported video interface or operating system to another, providing platform flexibility and protecting the original development investment. .NET development Included in MIL is a low-overhead API layer for developing Windows applications within the .NET Framework using managed Visual Basic and Visual C# code. JIT compilation and scripting MIL supports C# and Visual Basic JIT compilation and CPython scripting, facilitating experimentation and prototyping. Such code can even be executed from within a MIL-based application, providing a simpler way to tailor an already-deployed application. Simplified platform management With MIL, a developer does not require in-depth knowledge of the underlying platform. MIL is designed to deal with the specifics of each platform and provide simplified management (e.g., hardware detection, initialization, and buffer copy). MIL gives developers direct access to certain platform resources such as the physical address of a buffer. MIL also includes debugging services (e.g., function parameter checking, tracing, and error reporting), as well as configuration and diagnostic tools.
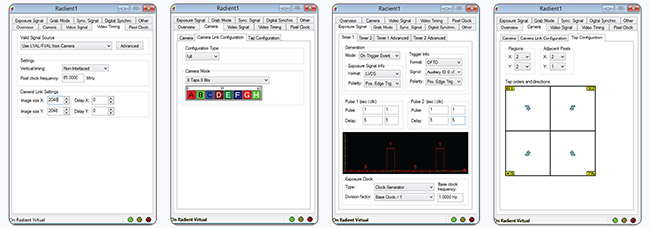
Designed for multi-tasking MIL supports multi-processing and multi-tasking programming models, namely, multiple MIL applications not sharing MIL data or a single MIL application with multiple threads sharing MIL data. It provides mechanisms to access shared MIL data and ensure that multiple threads using the same MIL resources do not interfere with each other. MIL also offers platform-independent thread management for enhancing application portability. Supported data formats MIL can manipulate data, such as monochrome images, stored in 1-, 8-, 16-, and 32-bit integers, as well as 32-bit floating point formats. MIL can also handle color images stored in packed or planar RGB / YUV formats. Commands for efficiently converting between data types are included. Saving and loading images MIL supports the saving and loading of individual images or sequence of images to and from disks. Supported file formats are AVI (Audio Video Interleave), BMP (bitmap), JPG (JPEG), JP2 (JPEG2000), MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14), native (MIM), PNG, and TIF (TIFF), as well as a raw format. Industrial and robot communication MIL lets applications interact directly with automation controllers using the EtherNet / IP™, MODBUS®, and PROFINET industrial communication protocols. It also supports native communication with robot controllers from ABB, DENSO, EPSON, FANUC, KUKA, and Stäubli. WebSocket access MIL allows an application to publish MIL object data for access from a browser or another standalone application using the HTML-5 WebSocket communication protocol. It uses a clientserver architecture where the server is the MIL-based application and the client is a JavaScript program running in a browser or a standalone application. The functionality can be used locally on the same device running the MIL-based application or remotely on another device that does not have MIL installed on it. The API extension supports client-side programming in JavaScript or C/C++. The MIL objects supported are the buffer and display ones. The functionality serves to view and interact with a MIL display (i.e., pan, scroll, zoom, etc.). Flexible and dependable image capture There are many ways to transmit video to an imaging system: Analog, Camera Link, Camera Link HS, CoaXpress, DVI-D, GigE Vision, SDI, and USB3 Vision. MIL supports all these interfaces either directly through Matrox Imaging or third-party hardware. MIL works with images captured from virtually any type of color or monochrome source including standard, high-resolution, high-rate, frame-on-demand cameras, line scanners, slow scan, and custom designed devices. For greater determinism and the fastest response, MIL provides multi-buffered image capture control performed in the operating system’s kernel mode. Image capture is secured for frame rates measured in the thousands per second even when the host CPU is heavily loaded with tasks such as HMI management, networking and archiving to disk. The multi-buffered mechanism supports callback functions for simultaneous capture and processing even when the processing time occasionally exceeds the capture time. Matrox Intellicam MIL features the Matrox Intellicam image capture and frame grabber configuration utility. This Windows-based program lets users interactively configure Matrox image capture hardware for a variety of image sources or simply try one of the numerous ready-made interfaces available from Matrox Imaging.
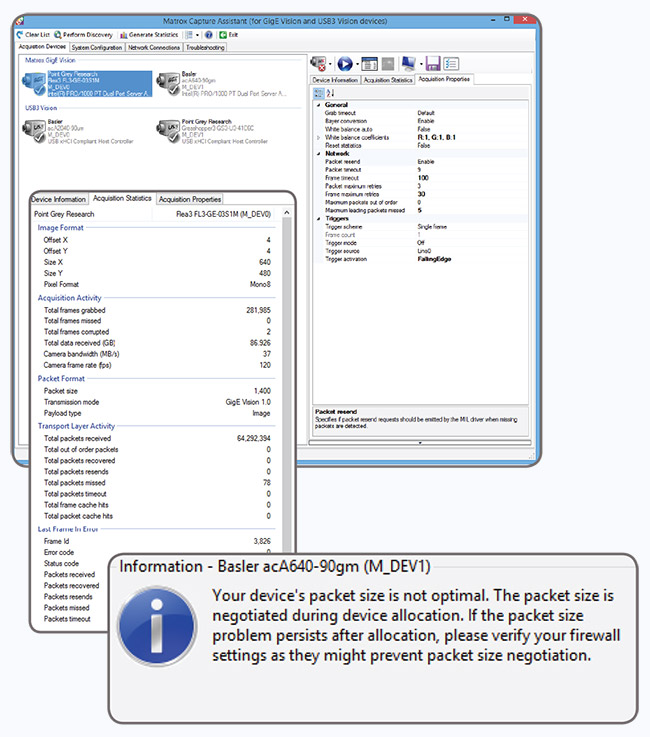
Matrox Capture Assistant MIL includes Matrox Capture Assistant, a Windows-based utility for verifying the connection to one or more GigE Vision or USB3 Vision cameras and testing video acquisition. It can obtain GigE Vision and USB3 Vision device information, collect and present acquisition statistics, and provide access to acquisition (GenICam™) properties. The gathering and display of statistics can be performed when acquiring within or outside of Matrox Capture Assistant. Matrox Capture Assistant also allows the adjustment of GigE Vision driver settings and provides the means to troubleshoot connectivity issues.
Simplified image display MIL provides transparent image display management with automatic tracking and updating of image display windows at live video rates. MIL also allows for live image display in a user-specified window. Display of multiple video streams using multiple independent windows or a single mosaic window is also supported. Moreover, MIL provides non-destructive graphics overlay, suppression of tearing artifacts, and filling the display area at live video rates. All of these features are performed with little or no host CPU intervention when using appropriate graphics hardware. MIL also supports multi-screen display configurations that are in an extended desktop mode (i.e., desktop across multiple monitors), exclusive mode (i.e., monitor not showing desktop but dedicated to MIL display), or a combination.
Graphics, regions, and fixtures MIL provides a feature-rich graphics facility to annotate images and define regions of operation. This capability is used by the MIL analysis tools to draw settings and results onto an image. It is also available to the programmer for creating application-specific image annotations. The graphics facility supports different shapes—dot, line, polyline, polygon, arc, and rectangle—and text with selectable font. It takes image calibration into account, specifically the unit, reference coordinate system, and applicable transformations. The graphics scale smoothly when zooming to sub-pixel. An interactive mode is available to easily allow developers to provide user editing of graphics: Add, move, resize, and rotate graphic elements. Moreover, the application can hook to interactivity-related events to automatically initiate underlying actions. The graphics facility can further be used to define Regions to guide or confine subsequent MIL analysis operations. Regions can also be repositioned automatically by tying its reference coordinate system to the positional results of a MIL analysis operation.
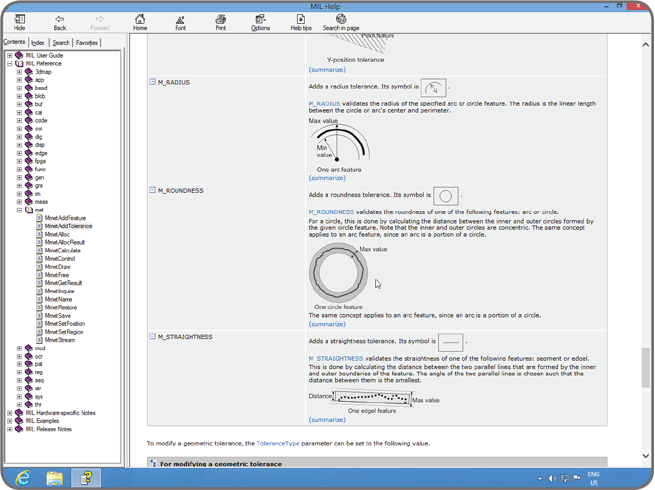
Application deployment MIL offers a flexible licensing model for application deployment. Only the components required to run the application need to be licensed. License fulfillment is achieved using a pre-programmed dongle or an activation code tied to Matrox Imaging hardware (i.e., smart camera, vision controller, I/O card, frame grabber, or dongle). Some components are pre-licensed with certain Matrox Imaging hardware; please consult the individual Matrox Imaging hardware datasheets for details. The use of Distributed MIL within the same physical system does not require the additional specific license. The installation of MIL can even be hidden from the end user. Documentation, IDE integration, and examples MIL’s online help provides developers with comprehensive and easy-to-find documentation, and online help can even be tailored to match the environment in use. The online help can be called up from within Visual Studio to provide contextual information on the MIL API. Also supported is Visual Studio’s intelligent code-completion facility, giving a programmer on-the-spot access to relevant aspects of the MIL API. An extensive set of categorized and searchable example programs allow developers to quickly get up to speed with MIL.
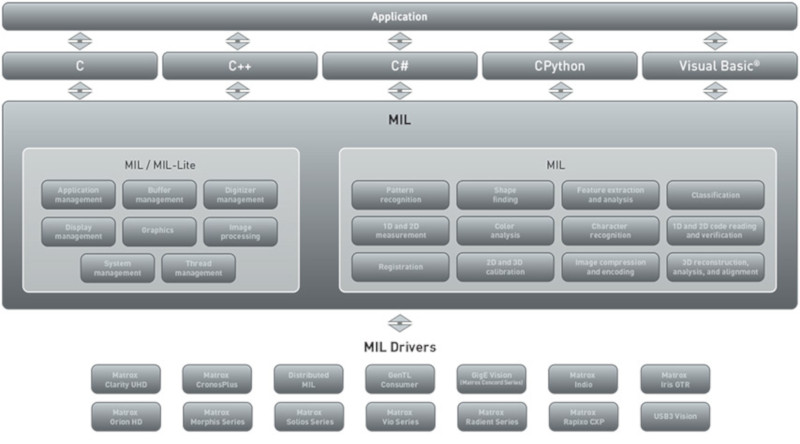
MIL-Lite MIL-Lite is a subset of MIL, featuring programming functions for performing image capture, annotation, display, and archiving. It also includes fast operators for arithmetic, Bayer interpolation, color space conversion, de-interlacing, temporal filtering, basic geometric transformations, histogram, logic, LUT mapping, and thresholding. MIL-Lite is licensed for both application development and deployment in the presence of Matrox Imaging hardware or a supplemental license tied to a dongle. Software architecture MIL provides a comprehensive set of application programming interfaces, imaging tools and hardware support
TRAINING AND SUPPORT Matrox Vision Academy Matrox Vision Academy provides all the expertise of live classroom training, with the convenience of on-demand instructional videos outlining how to get the most out of MIL vision software. Available to customers with valid MIL maintenance subscriptions, as well as those evaluating the software, users can seek out training on specific topics of interest, where and when needed. Regularly scheduled live classroom training is also offered at Matrox Imaging Headquarters. Matrox Vision Academy aims to help users increase productivity, reduce development costs, and bring applications to market sooner. For more information, visit https://info.matrox.com/imaging/form/vision-academy.
Matrox Professional Services Matrox Professional Services delivers deep technical assistance and customized trainings to help customers develop their particular applications. These professional services comprise personalized training; assessing application or project feasibility (e.g., illumination, image acquisition, and vision algorithms); demo / prototype applications / projects; troubleshooting, including remote debugging; and video / camera interfacing. Backed by the Matrox Vision Squad—a team of high-level vision professionals—Matrox Professional Services offer more in-depth support, recommending best methods with the aim of helping customers save valuable development time and deploy solutions more quickly. For more information on pricing and scheduling, contact Matrox Sales at https://www.matrox.com/imaging/en/buy/representatives/.
MIL maintenance program MIL users have access to a Maintenance Program, renewable on a yearly basis. This maintenance program entitles registered users to free software updates and entry-level technical support from Matrox Imaging, as well as access to Matrox Vision Academy. For more information, please refer to the Matrox Imaging Software Maintenance Programs brochure or visit www.matrox.com/imaging/en/support/support_maintenance/.
SUPPORTED ENVIRONMENTS For Windows:
For RTX64:
For Linux:
MIL for real-time Windows MIL is available to run natively in IntervalZero’s RTX64 real-time operating system platform for Windows. RTX64 runs on its own dedicated CPU core(s) alongside Windows to provide a more tightly bound deterministic environment. Under this architecture, a developer partitions a MIL-based application to run on RTX64 and Windows. Response-critical parts are performed in RTX64. These include image capture, processing, and analysis and, more significantly, output activation and real-time communication. Less response-critical aspects such as image display and file I/O continue to be conducted in Windows.Development for RTX64 is done in C / C++ using Visual Studio and a subset of the Windows API. MIL for RTX64 supports image capture using GigE Vision. Distributed MIL’s shared memory protocol is available to efficiently handle communication and data exchange, including images, between a MIL process running on RTX64 and one running on Windows. The required MIL licenses are shared between Windows and RTX64.
Ordering Information MIL 10 Development Toolkits
MIL-Lite 10 Development Toolkits
Matrox Vision Academy Training
MIL / MIL-Lite Maintenance Program
Note: 50% educational discount for MILMAINTENANCE and LTEMAINTENANCE with proof of affiliation with an academic institution. MIL 10 Run-Time Licenses / MIL-Lite 10 Supplemental Licenses Software license keys
For more information contact CRI Jolanta by phone at: +48 32 775 0371, by email info@crijolanta.com.pl, or by contact form. Software |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||